You buy gadgets on Amazon and get groceries from Walmart, but did you know you can hire a hacker online? It’s easy to find forums and dark web marketplaces advertising hacking services to recover passwords, access restricted accounts, or disrupt competitors.
While the ability to hire a hacker might seem like a convenient solution for digital problems, these services often mask a darker reality. What may appear as a quick fix can turn into a costly and even dangerous decision.

Warning: Hiring a hacker can unintentionally involve you in much larger and more dangerous criminal networks. By engaging with these hackers, you may unknowingly contribute to larger criminal enterprises, increasing your exposure to law enforcement investigations.
1. Who Would Hire a Hacker, and Why?
Most people don’t think about hiring a hacker. However, the concept has grown beyond underground subcultures. For some, the decision to hire a hacker could be a practical one, such as regaining access to lost services.
Individuals, groups, or organizations may have compelling reasons to hire a hacker as the digital world becomes increasingly complex.
For example:
- Personal: It may be as innocent as recovering passwords to locked-out social media accounts. However, some also request hackers spy on a partner’s account.
- Corporate: The incentive to hire a hacker can be tied to competitive advantages. Businesses may seek to spy on competitors by infiltrating emails or sabotaging a rival’s online presence.
- Hacktivism: Hacking driven by political or ideological reasons has increased, with hackers targeting government sites or media outlets.
a. Services That Hackers May Offer
The range of hacking services available online is vast, catering to nearly every digital dilemma imaginable:
- Unauthorized Access: Gaining unauthorized access to private accounts, corporate networks, or databases.
- Disruptive Attacks: Some hackers can carry out Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and prevent websites from working correctly.
- Data Theft: Acquiring personal data, often used to exploit or impersonate others for financial or personal gain.
- Social Media Manipulation: Modifying social media profiles, retrieving deleted messages, or even “hacking” follower counts to boost influence.
b. How Hackers Protect Their Identities
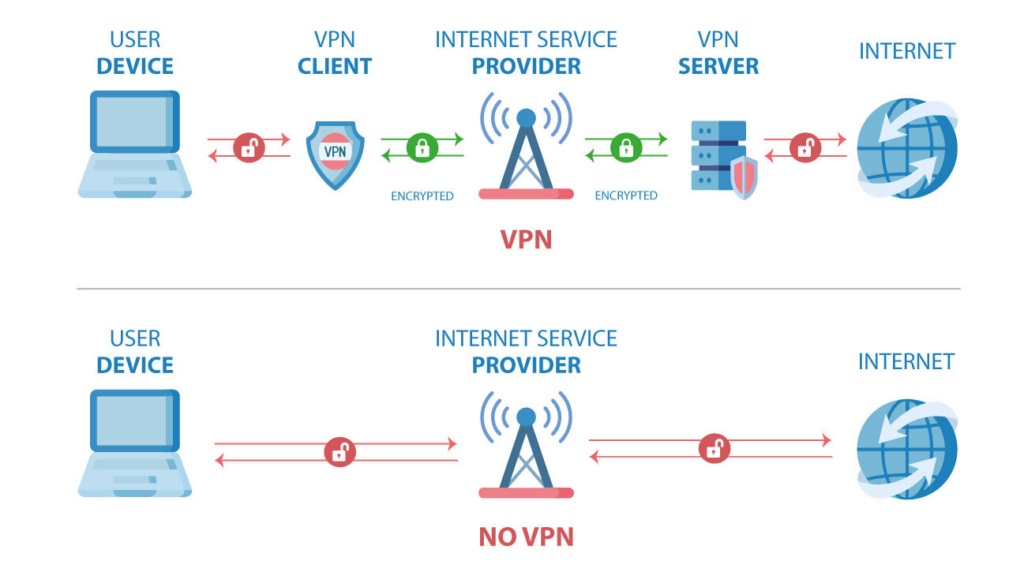
Hackers employ several methods designed to anonymize their activities and interactions with clients to avoid detection and protect their identities. For example,
- Pseudonyms and Aliases: Hackers rarely use their real names online. Instead, they operate under multiple pseudonyms and aliases, frequently changing them.
- Cryptocurrency Payments: Most hacking transactions use anonymous payment methods like cryptocurrencies.
- VPNs and Proxy Servers: Hackers use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and proxy servers to hide their locations, making it difficult to track their real identities.
- Encrypted Communication: Hackers insist on communicating through encrypted channels to protect the privacy of their conversations.
Thinking of Hiring a Hacker?
Avoid the risks of hiring hackers and safeguard your data with NordVPN. Get secure, anonymous browsing and protect your personal information from cyber threats.
2. Where to Hire a Hacker
The growing demand for illicit hacking services has given rise to a network of platforms where hackers advertise their skills. You may assume these services are confined to the dark web, but they’ve increasingly surfaced in more accessible corners of the internet.
Platforms you may find them on include:
a. Dark Web Marketplaces
The dark web remains the primary hub for hacking services. Marketplaces accessible only through Tor browsers allow users to browse offerings, from simple password recovery to more complex services like launching DDoS attacks or breaching corporate networks.
These marketplaces function similarly to eCommerce platforms, with hackers providing detailed descriptions of their services, user reviews, and cryptocurrency payment options to ensure anonymity.
Some examples include:
- Dream Market (now defunct)
- STYX Market
- BidenCash
b. Encrypted Messaging Apps
Another method for hiring hackers is through encrypted messaging platforms like Telegram, Signal, and Wickr. Hackers often use these apps to engage directly with potential clients, offering more tailored services or ongoing communication.
These platforms are preferred for their end-to-end encryption, making it difficult for law enforcement to intercept or monitor conversations. Some hacking groups create private channels, inviting users interested in their services.
Popular encrypted messaging apps include:
c. Surface Web Forums and Social Media
Surprisingly, some hackers advertise their services on the surface web, using forums, social media platforms, and even public discussion boards. While these posts may be more discreet, they offer the same illegal activities found on the dark web.
Social media platforms like Facebook, BlackHatWorld, and Reddit have seen increasing activity from these hackers. However, they may be challenging for outsiders since they use code words and indirect marketing to avoid detection.
d. Freelance and Gig Economy Platforms
In some cases, hacking services have infiltrated legitimate freelance platforms like Fiverr or Upwork, where individuals offer “ethical hacking” services that cross into illegal activities. Once identified, these postings are usually removed.
However, they often reappear under various guises, making it difficult for these platforms to eliminate the problem. Hackers use these platforms to offer services like email or account recovery, but the scope of work often exceeds legal boundaries.

3. Should You Hire a Hacker?
While hiring a hacker may seem like an easy solution to problems, it often comes with significant risks. Cybercrime laws worldwide are strict, targeting hackers and their clients. On top of that, working with someone who has such skills inevitably creates vulnerabilities for you.
Issues you may face are:
- Possibility of Scams: Many hackers operate anonymously, and you have no idea if they’re credible or competent. They could even disappear after receiving payment, leaving you nothing in return.
- Blackmail and Extortion: Once a hacker gains access to sensitive personal or business data, they may threaten to release the information unless additional payments are made.
- Planting Backdoors: Hackers often install malware, such as keyloggers, onto devices they claim to help with. This gives access even after the initial service has been delivered.
- Potential Escalation: Hackers are often driven by their incentives and may escalate the situation in unexpected and dangerous ways.
- Risk of Retaliation: Some of those targeted by hackers may retaliate, especially if they have the means or connections to do so.
4. Cost of Hiring a Hacker
The cost to hire a hacker varies significantly depending on the type of service requested, the hacker’s expertise, and the risks involved. Prices can range from as low as $100 for simple tasks like social media account access to thousands for more complex operations.
Prices can vary widely, but here are some rough guidelines:
- Social Media and Email Access: $100 – $500
- Website Hacking: $1,000 – $10,000+
- Information Theft: $2,000 – $20,000+
- DDoS Attacks: $500 – $5,000
- Corporate Espionage/Sabotage: $10,000 – $50,000+
- Customized Services: $5,000 – $50,000+
5. Legal Consequences of Hiring a Hacker
Hiring a hacker for unethical purposes poses significant legal risks. Many underestimate the severity of these consequences, assuming that anonymity on the internet or the dark web will shield them from liability.
However, this is rarely the reality. The chances are high that you will get caught. And when you do, here are some potential consequences:
- Criminal Charges: Those who hire a hacker are seen as complicit in the crime and often face charges if caught.
- Financial Penalties: You may be ordered to compensate victims for monetary losses, legal fees, and damages from a hack.
- Civil Lawsuits: Individuals who hire hackers often face civil lawsuits from the victims of the hack, which can result in significant settlements or damage awards.
- Cross-Border Complications: If you hire a hacker overseas, you may face extradition to the victim’s country for prosecution.
- Reputational Damage: For businesses, hiring a hacker and getting caught can lead to loss of clients, partnerships, and, in severe cases, business closure.
- Long-Term Digital Surveillance: Getting caught, you may face digital restrictions or monitoring as part of your sentence. Say hello to Big Brother.
Stay Secure and Avoid Legal Risks
Don’t risk your security by engaging in illegal activities. NordVPN provides advanced encryption and
privacy tools, so you can browse safely and avoid data breaches.
6. The Exception: White Hat Hackers
While the term hacker often carries negative connotations, not all hackers operate on the wrong side of the law. Ethical hackers, also known as white hat hackers, use their skills to improve cybersecurity.
These professionals are critical to identifying and fixing digital system vulnerabilities. They aim to help protect individuals, businesses, and governments from cyber threats. Because of this, they operate with permission and within legal frameworks.
a. What is Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hacking involves legally probing systems, networks, and applications to find security flaws that malicious actors could exploit. Ethical hackers use the same methods and techniques as criminal hackers, but with the owner’s consent and for a positive purpose.
By mimicking the actions of black hat hackers, ethical hackers can identify potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited in real-world attacks. Examples of ethical hacking include:
- Penetration Testing: White hat hackers attempt to breach a system’s defenses to identify vulnerabilities. They then provide detailed reports and suggestions for improving security.
- Red Team vs. Blue Team: Ethical hackers simulate an attack while the internal security team defends. These exercises help organizations improve their incident response strategies and overall cybersecurity preparedness.
b. When Does Hacking Become Unethical?
While ethical hackers operate within legal and moral boundaries, the line between ethical and unethical hacking can sometimes blur. Ethical hackers must obtain explicit permission from system owners before conducting any tests.
Without permission, even well-intentioned hacking becomes illegal and could lead to severe consequences. When this happens, it’s considered as Grey Hat hacking.
7. Final Thoughts
While the temptation to hire a hacker for quick, less ethical solutions may seem appealing, remember that significant risks are present. These risks often far outweigh the potential benefits of hiring a hacker.
Engaging with a hacker to steal data, sabotage competitors, or access restricted accounts can lead to severe legal consequences, long-term security risks, and ethical dilemmas that can harm your reputation and innocent people around you.
Rather than taking the risky and illegal route of hiring a hacker, legitimate alternatives provide the same results without crossing legal or ethical boundaries.
Share this content:
